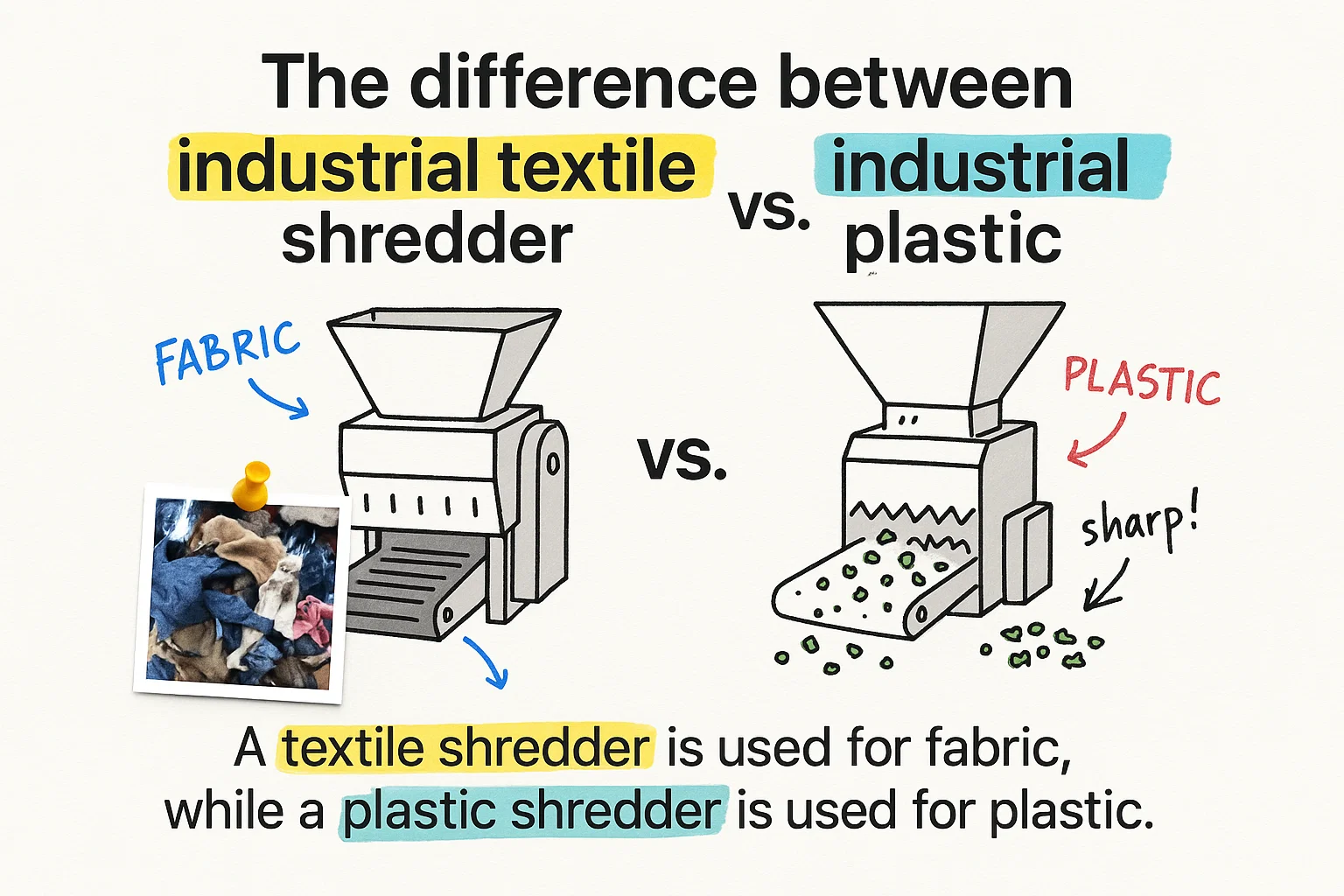
La diferencia entre una trituradora textil y una trituradora estándar es fundamental cuando se procesan materiales que requieren mecanismos de corte especializados. Los residuos textiles requieren una capacidad de trituración única que las trituradoras industriales estándar simplemente no pueden ofrecer. Si manipula retales de tela, residuos de prendas de vestir o materiales de fibra, la elección de una trituradora incorrecta conlleva atascos frecuentes, un mantenimiento excesivo y costosos tiempos de inactividad que pueden paralizar sus operaciones de reciclaje.
En Máquina Rumtoo, Hemos diseñado trituradoras estándar y específicas para textiles en cientos de instalaciones de todo el mundo. Esta guía desglosa las diferencias técnicas, los escenarios de aplicación y las consideraciones de coste para ayudarle a seleccionar el equipo adecuado para su flujo de materiales.
¿Qué diferencia a las destructoras textiles de las destructoras estándar?
Las trituradoras textiles cuentan con diseños de rotor especializados y geometrías de corte que evitan que el tejido se enrolle alrededor del eje. Las trituradoras estándar utilizan configuraciones de dientes agresivas optimizadas para materiales rígidos como plásticos, madera o metal. Cuando se introducen textiles blandos y flexibles en una trituradora estándar, el material se enrolla alrededor del rotor en lugar de cortarlo limpiamente.
La diferencia clave radica en el ángulo y la separación de las cuchillas. Las trituradoras textiles emplean cuchillas en forma de gancho colocadas a intervalos más amplios, que agarran y desgarran los materiales fibrosos sin crear tensiones que provoquen enrollamientos. Las trituradoras estándar utilizan cuchillas en forma de V o planas colocadas a menor distancia entre sí, diseñadas para fracturar materiales duros mediante la fuerza de impacto y cizallamiento.
Requisitos de velocidad y par del rotor
Las trituradoras textiles funcionan a velocidades de rotación más bajas, normalmente entre 40 y 80 RPM, con un par elevado para arrastrar el material a través de la cámara de corte. Esta acción lenta y potente evita que el material rebote o se enrede. Las trituradoras estándar funcionan a mayor velocidad, a menudo entre 80 y 150 RPM, porque los materiales rígidos requieren una velocidad de impacto más que una fuerza de tracción sostenida.
Las especificaciones de su motor reflejan esta diferencia. Una trituradora textil que procese 500 kg/hora de residuos de tejidos necesita aproximadamente 30-45 kW de potencia con una caja de engranajes de alto par. Una trituradora estándar que procese el mismo caudal de plásticos rígidos funciona eficazmente con 22-30 kW porque la acción de corte requiere menos fuerza sostenida.
Capacidades de manipulación de materiales: En qué destaca cada trituradora
Aplicaciones de la trituradora textil:
- Retazos de tela post-industrial
- Ropa y calzado al final de su vida útil
- Residuos de alfombras y tapicerías
- materiales no tejidos
- Residuos de cuerdas y cordeles
- Colchones y ropa de cama
Aplicaciones de la trituradora estándar:
- Botellas y envases de plástico rígido
- Madera y palés de madera
- Recintos para residuos electrónicos
- Latas y bidones metálicos
- Piezas de automóvil (parachoques, salpicaderos)
- escombros de construcción
Según la Agencia de Protección del Medio Ambiente de EE.UU., Los residuos textiles representan más de 11,3 millones de toneladas anuales en los flujos de residuos sólidos urbanos. Procesar este volumen requiere equipos específicamente diseñados para materiales fibrosos, ya que las trituradoras estándar experimentarían constantes fallos de funcionamiento.
Tamaño de la criba y consistencia de las partículas de salida
El tamaño de perforación de la criba difiere significativamente entre estos tipos de trituradoras. Las trituradoras textiles utilizan orificios de criba más grandes, normalmente de 50 mm a 100 mm, porque el tejido compactado necesita espacio para pasar sin crear contrapresión. Las trituradoras estándar emplean cribas más estrechas, a menudo de 20 mm a 50 mm, para conseguir un tamaño uniforme de las partículas de materiales rígidos.
Cuando se procesan textiles a través del tamiz estanco de una trituradora estándar, el material se comprime y obstruye las perforaciones. Esto crea un efecto de asfixia que sobrecarga el motor y detiene la producción. Las trituradoras textiles solucionan este problema permitiendo la salida rápida de material parcialmente triturado, que puede volver a procesar si necesita partículas de menor tamaño.
Impacto en el mundo real: Una fábrica de confección de Carolina del Norte cambió una destructora estándar reutilizada por una destructora textil específica. El tiempo de inactividad por atasco se redujo de 6 horas por turno a menos de 30 minutos por semana. La producción de material aumentó en 240%, mientras que el consumo de energía por tonelada se redujo en 18%.
Diseño del sistema de alimentación y consideraciones de seguridad
Las trituradoras textiles incorporan tolvas de alimentación anchas y de ángulo bajo que permiten la entrada sin problemas de materiales voluminosos como prendas enteras o rollos de alfombra. El diseño de la tolva impide que el material se atasque o quede colgando en la entrada. Las trituradoras estándar incorporan tolvas más inclinadas y estrechas optimizadas para objetos rígidos que fluyen libremente y no se comprimen ni expanden.
Los mecanismos de seguridad también difieren. Las trituradoras textiles incluyen sistemas de detección que detectan un par excesivo del material envuelto e invierten automáticamente el rotor para eliminar el atasco. Las trituradoras estándar se centran en la protección contra objetos extraños duros, como cierres metálicos o piedras, mediante sistemas de cilindros hidráulicos y embragues de sobrecarga.
Acceso para mantenimiento y sustitución de piezas de desgaste
Las cuchillas de las trituradoras textiles se cambian con más frecuencia porque el tejido contiene contaminantes abrasivos como arena, botones y cremalleras. La vida útil de las cuchillas oscila entre 200 y 400 horas de funcionamiento en función de la limpieza del material. Las trituradoras estándar que procesan plásticos rígidos limpios alcanzan de 800 a 1.200 horas entre cambios de cuchillas.
Las trituradoras textiles ofrecen paneles de acceso rápido y diseños de rotor modulares que permiten cambiar las cuchillas sin desmontar el conjunto del rotor. Esto reduce el tiempo de inactividad por mantenimiento a 2-3 horas frente a las 6-8 horas de desmontaje completo del rotor. Las trituradoras estándar requieren un mantenimiento menos frecuente, pero suelen requerir un desmontaje más extenso cuando es necesario sustituir las cuchillas.
Comparación de especificaciones técnicas
| Especificación | Trituradora textil | Trituradora estándar |
|---|---|---|
| Velocidad del rotor | 40-80 RPM | 80-150 RPM |
| Configuración de Cuchillas | Forma de gancho, amplia separación | En forma de V o planas, poco espaciadas |
| Apertura de pantalla | 50-100 mm | 20-50 mm |
| Potencia del motor (500 kg/h) | 30-45 kW | 22-30 kW |
| Vida de la Cuchilla | 200-400 horas | 800-1.200 horas |
| Rendimiento típico | 300-1.000 kg/h | 500-2.000 kg/h |
Análisis de costes: Inversión inicial frente a gastos de explotación
Las trituradoras textiles suelen costar entre 15 y 25% más que las trituradoras estándar comparables, debido a su ingeniería especializada y a los menores volúmenes de producción. Una trituradora textil de capacidad media (500 kg/h) oscila entre $45.000 y $75.000, mientras que una trituradora estándar con un rendimiento similar cuesta entre $35.000 y $55.000.
Sin embargo, utilizar el tipo de equipo equivocado multiplica los costes. Las instalaciones que intentan procesar textiles con trituradoras estándar declaran unos gastos de mantenimiento 3-4 veces superiores a lo que sugieren las especificaciones. La frecuencia de sustitución de las cuchillas se duplica o triplica, las reparaciones del motor aumentan y los costes de mano de obra para eliminar atascos se acumulan rápidamente.
Patrones de consumo de energía
A pesar de la mayor potencia del motor, las trituradoras textiles suelen consumir menos energía por tonelada de material procesado. El funcionamiento a bajo régimen y par elevado mantiene un consumo constante sin las sobrecargas que se producen cuando las trituradoras estándar se enfrentan a materiales difíciles. Sus instalaciones tendrán una demanda eléctrica más estable y podrán reducir los picos de demanda.
Las trituradoras estándar demuestran una eficiencia energética superior cuando procesan los materiales a los que están destinadas. Una trituradora estándar que procesa envases rígidos de HDPE consume aproximadamente entre 15 y 22 kWh por tonelada, mientras que una trituradora textil que procesa residuos textiles consume entre 25 y 35 kWh por tonelada debido a la baja densidad aparente y la alta compresibilidad del material.
Cuándo elegir una destructora estándar para flujos de residuos mixtos
Algunas operaciones de reciclado manejan tanto plásticos rígidos como pequeñas cantidades de contaminación textil. En estos casos, una trituradora estándar con funciones de tolerancia textil es la mejor solución. Busque modelos con:
- Función de rotor reversible para limpiar el material envuelto
- Aperturas de criba más grandes (40-60 mm) que equilibran el tamaño de las partículas con el rendimiento.
- Velocidad de rotor moderada (60-90 RPM) que maneja ambos tipos de materiales
- Protección del motor mejorada contra condiciones de sobrecarga temporal
Este compromiso funciona cuando los textiles representan menos de 10-15% de su flujo de entrada. Por encima de ese umbral, experimentará suficientes problemas operativos para justificar un triturador de textiles dedicado o un sistema de procesamiento en dos etapas.
Elija el Triturador Correcto para Su Flujo de Materiales
Rumtoo Machine fabrica tanto trituradores específicos para textiles como trituradores estándar, diseñados para operaciones industriales continuas. Nuestro equipo cuenta con sistemas de cambio de cuchillas rápidos, detección automática de atascos y monitoreo predictivo de mantenimiento.
Ofrecemos un diseño de sistema completo, incluyendo transportadores, recopilación de polvo y equipo de separación downstream. Cada instalación incluye capacitación para operadores, paquetes de piezas de repuesto y cobertura de garantía de 24 meses.
Consulte nuestras especificaciones completas de triturador y obtenga una cotización personalizada →
Sistemas Híbridos para Máxima Flexibilidad
Las grandes instalaciones de reciclaje cada vez más instalan líneas de procesamiento paralelas con ambos tipos de trituradores. Esta configuración dirige los materiales al equipo adecuado según su composición, maximizando la capacidad de producción y minimizando problemas de mantenimiento. Un sistema de clasificación automática en el flujo de entrada dirige los textiles a una línea y los materiales rígidos a otra.
La inversión inicial para sistemas dobles es 60-80% mayor que las instalaciones de un solo triturador, pero las instalaciones que procesan 5+ toneladas por día suelen recuperar la inversión en 18-24 meses a través de un tiempo de actividad mejorado y costos de mantenimiento reducidos. También ganan flexibilidad para aceptar diferentes flujos de residuos que requieren tarifas de vertido premium.
Consideraciones entre Single-Shaft y Dual-Shaft
Tanto los trituradores específicos para textiles como los estándar vienen en configuraciones de un solo eje y de doble eje. Los diseños de un solo eje con cilindro hidráulico producen un tamaño de partícula más uniforme y funcionan bien para materiales que requieren un procesamiento adicional. Los trituradores de doble eje ofrecen una mayor capacidad de producción y mejor manejo de materiales contaminados, pero generan una salida menos consistente.
Para aplicaciones textiles, los trituradores de doble eje dominan porque los residuos de ropa contienen broches metálicos, botones y otros contaminantes que una máquina de un solo eje necesitaría eliminar en el flujo upstream. Sin embargo, los trituradores textiles de un solo eje con sistemas de alimentación hidráulica y funciones de reversión automática pueden manejar eficazmente residuos de alfombras y tejidos con outputs de producción que van desde 300-1,500 kg/h. Los trituradores estándar que sirven a operaciones de reciclaje de plástico prefieren diseños de un solo eje cuando el flujo de materiales es relativamente limpio y consistente.
Tome la Decisione Correcta de Equipamiento para Su Operación
Elegir entre trituradores específicos para textiles y estándar requiere una evaluación honesta de su composición actual de materiales y planes de procesamiento futuros. Comience analizando su flujo de residuos durante un período de dos semanas, documentando el porcentaje de materiales fibrosos en comparación con componentes rígidos.
Si los textiles superan el 20% de su volumen, especifique un triturador específico para textiles. Para flujos mixtos con 5-15% textiles, considere un triturador estándar con características mejoradas. Las operaciones que procesan residuos textiles puros deben evaluar únicamente equipo específico para textiles para evitar problemas operativos crónicos.
Calcule su costo total de propiedad durante un período de cinco años, incluyendo energía, mantenimiento, cambio de cuchillas y tiempo de inactividad. El equipo con el precio de compra más bajo rara vez ofrece el mejor valor cuando se procesan el tipo incorrecto de materiales. Tenga en cuenta sus costos laborales para la eliminación de atascos, que pueden alcanzar $15,000-$25,000 anualmente con equipo no adecuado.
Conclusión Principal: La diferencia entre el triturador de textiles y el triturador estándar va más allá del diseño de las cuchillas. Estas máquinas representan enfoques fundamentalmente diferentes para la reducción de tamaño, optimizados para características específicas de materiales. La selección de equipo que se ajuste a su flujo de materiales determina si su operación de reciclaje es rentable o lucha con problemas de mantenimiento constantes y baja capacidad de producción.
Su triturador es la base de su sistema de reciclaje. Tener una buena decisión en esta elección afecta todos los procesos downstream, desde la clasificación y limpieza hasta la calidad final del producto. Tómese el tiempo de trabajar con proveedores de equipos experimentados que entienden sus desafíos de materiales y pueden proporcionar referencias de aplicaciones similares.
Para obtener más información sobre la selección de equipos para reciclaje de plástico, visite nuestra guía completa sobre máquinas trituradoras de plástico.