The profitability of a recycling operation depends entirely on the feedstock. Mixing incompatible polymers (e.g., PVC with PET) can catastrophically damage extrusion equipment and render the final rPET flakes unsellable. For plant operators, mastering the ASTM International Resin Identification Coding System (RIC) is the first line of defense against contamination.
This guide analyzes the seven resin codes from an industrial processing perspective, detailing the specific recycling machines required for each polymer.
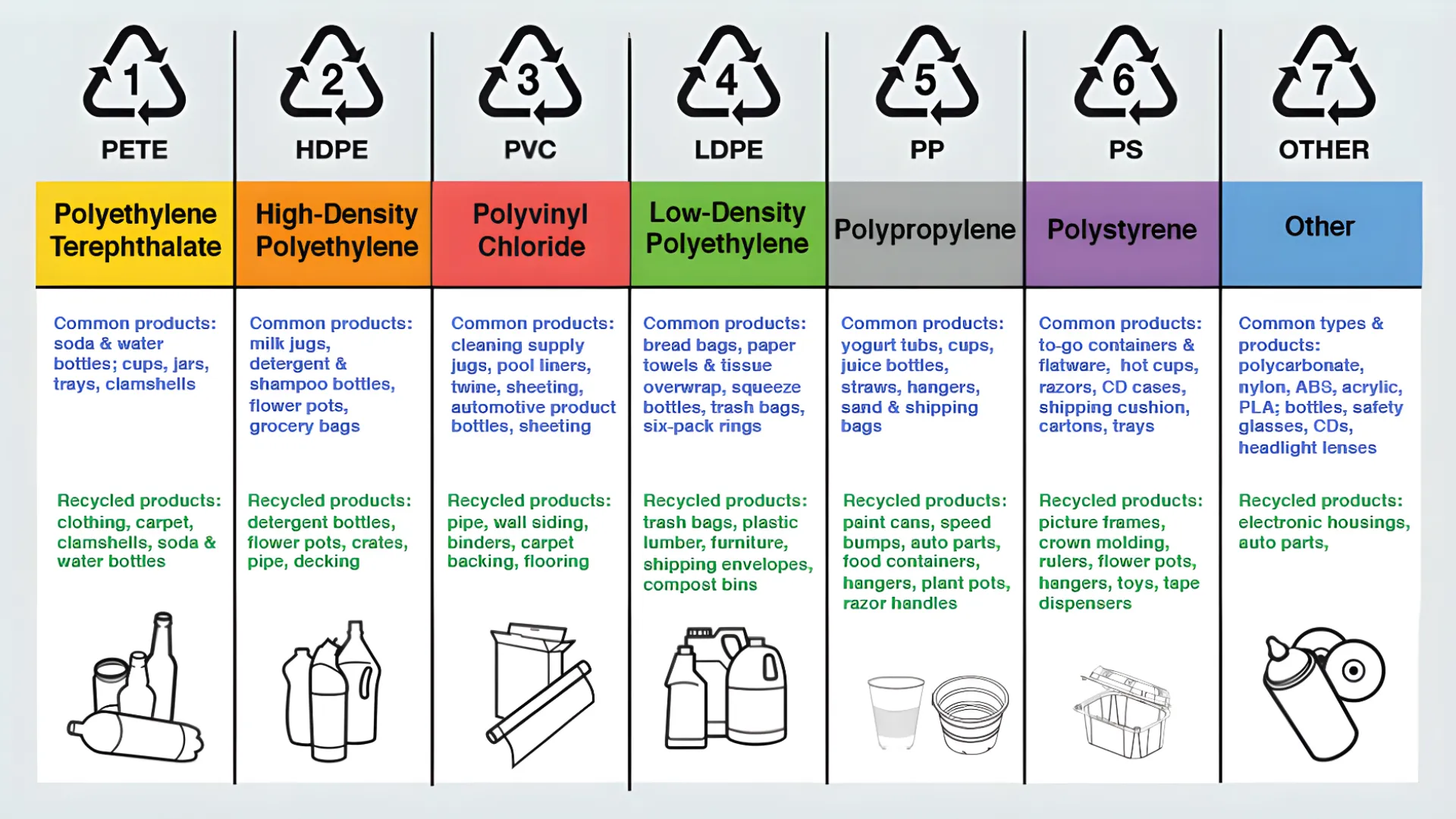
1. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)


- Source: Beverage bottles, food trays.
- Properties: High transparency, solvent resistance.
- Processing Requirement: Labels and glues are the primary contaminants. A PET Bottle Washing Line with a hot caustic wash is mandatory to achieve the purity levels (<50ppm PVC) needed for fiber or bottle-to-bottle applications.
2. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)


- Source: Detergent jugs, shampoo bottles, oil drums.
- Properties: High strength-to-density ratio, floats in water (density < 1.0 g/cm³).
- Processing Requirement: Rigid HDPE requires high-torque shearing. A Single Shaft Shredder is used for initial size reduction of thick lumps, followed by sink-float separation tanks.
3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)

- Source: Pipes, window profiles, cable insulation.
- Properties: Chlorine content makes it heat sensitive. Degradation releases hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- Processing Requirement: Avoid processing PVC in standard, general-purpose extruders. It requires specialized screw geometry and tight temperature control to prevent degradation. We recommend specialized PVC Granulators for size reduction.
4. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)


- Source: Shrink wrap, shopping bags, agricultural film.
- Properties: High ductility, low tensile strength.
- Processing Requirement: Films wrap around standard rotors. Use a designated Film Recycling Washing Line with an integrated varying-diameter screw press (squeezer) to mechanically dewater the fluff before pelletizing.
5. PP (Polypropylene)

- Source: Bottle caps, yogurt containers, car bumpers.
- Properties: High melting point, chemical resistance.
- Processing Requirement: Often co-mingled with PE. Sink-float tanks separate PP (floats) from PET (sinks).
6. PS (Polystyrene)
- Source: Expanded foam (EPS), disposable cutlery (HIPS).
- Processing Requirement: EPS is 98% air. It must be densified using a cold compactor or hot melt machine before it can be economically transported or granulated.
7. Other (Code 7)
Code 7 is a catch-all category for plastics that don’t fit neatly into #1–#6. It often includes engineered or “specialty” materials and multi-layer packaging.
- Common Materials: PC (polycarbonate), ABS, PA/Nylon, PMMA (acrylic), PLA (bioplastic), multi-layer composites.
- Recycling Reality: “Other” plastics are frequently incompatible with standard commodity recycling streams and are often rejected unless you have a dedicated, segregated feedstock and end-market.
- Processing Requirement: Treat Code 7 as a contamination risk unless it’s positively identified and separated. NIR optical sorting and strict bale specs are typically required before size reduction and extrusion.
Summary: Processing Compatibility Table
| Plastic | Density (g/cm³) | Float/Sink in Water | Primary Machine |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | 1.38 | Sink | Hot Washer |
| HDPE | 0.93 – 0.97 | Float | Shredder |
| PVC | 1.16 – 1.45 | Sink | Specialized Granulator |
| LDPE | 0.91 – 0.94 | Float | Film Squeezer |
| PP | 0.90 – 0.92 | Float | Sink-Float Tank |
| PS | 1.04 – 1.07 | Sink | Densifier / Hot Melt |
| Other | Varies | Varies | NIR Sorting / Dedicated Line |
At Rumtoo, we design entire turnkey systems based on these material properties. Understanding the chemistry of your waste stream allows us to configure the correct Recycling Machine for maximum ROI.