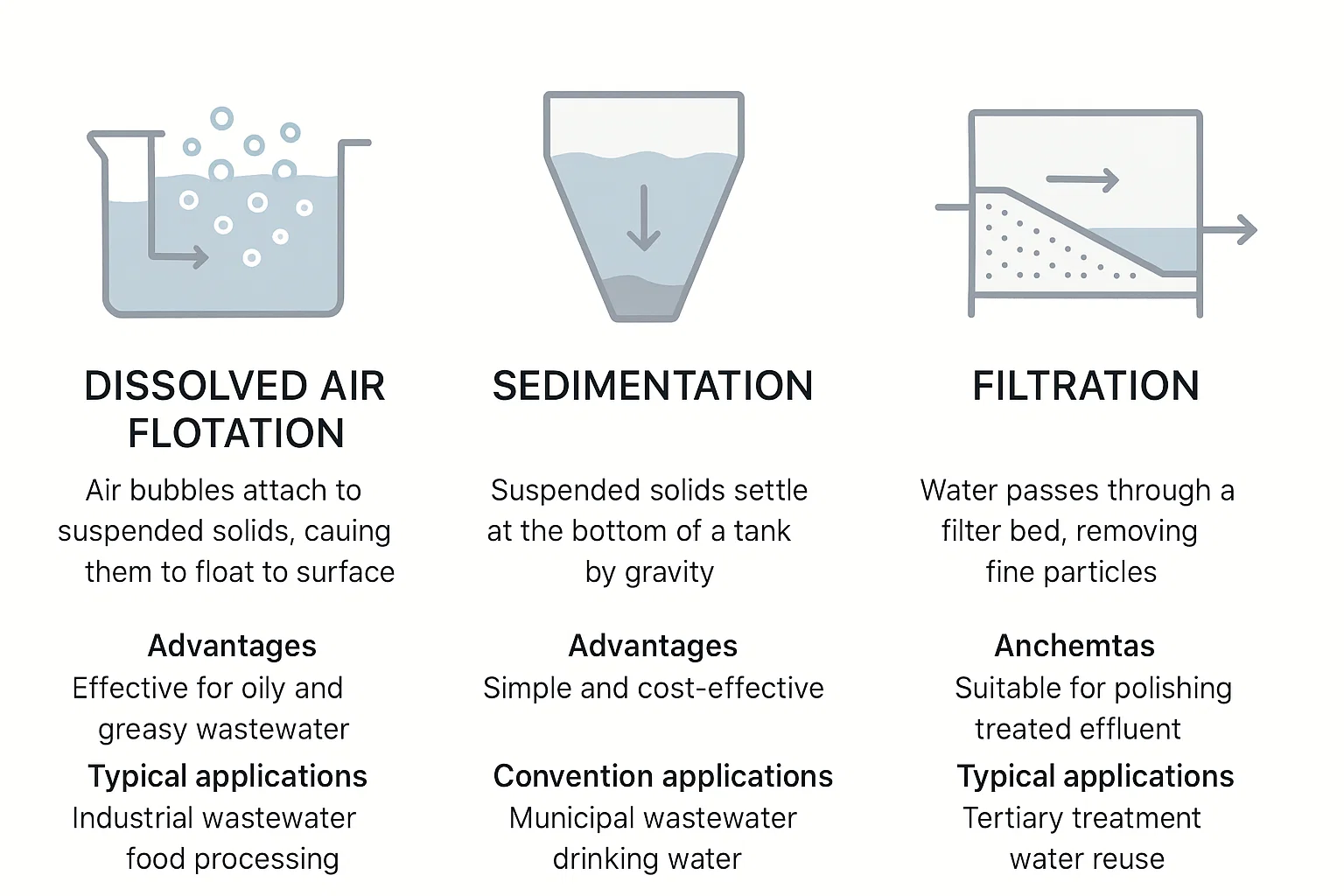
In the world of industrial wastewater treatment—especially within sectors like переработка пластика—choosing the right technology is critical. The effluent from plastic washing lines often contains fine plastic particles, label residues, oils, and suspended solids. Efficient treatment of this complex mixture not only ensures regulatory compliance but also improves operational sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
While conventional methods such as sedimentation и filtration still play vital roles, Флотация растворенным воздухом (DAF)has emerged as a robust and efficient alternative for tackling modern wastewater challenges.
Explore how DAF systems from Rumtoo outperform traditional approaches in both performance and practicality.
Technology Overview
Флотация растворенным воздухом (DAF)
DAF systems introduce microscopic air bubbles into wastewater. These bubbles attach to fine solids and oil droplets, causing them to float to the surface, where they are removed by skimming. It’s particularly effective for removing low-density and hydrophobic materials that are difficult to settle.
Седиментация
A gravity-driven process where heavier particles settle at the bottom of a basin. While energy-efficient, sedimentation is ineffective for light or colloidal particles and requires large infrastructure and long retention times.
Фильтрация
Water passes through a porous medium—ranging from sand filters to advanced membranes. Filtration is highly effective in removing very fine particles, bacteria, and dissolved solids, often used in the final (tertiary) stage of treatment or water reuse applications.
Comparative Performance Summary
| Особенность | ДАФ | Седиментация | Фильтрация |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Buoyancy (air bubbles float solids) | Gravity (solids settle) | Physical barrier (sieving) |
| Best For | Oils, grease, fine plastics, algae | Sand, grit, dense solids | Fine particles, pathogens, dissolved solids |
| TSS Removal Efficiency | Very High (90–99%) | Moderate (50–70%) | High to Very High (depending on type) |
| Footprint | Compact | Very Large | Variable (often compact) |
| Hydraulic Retention Time | 15–30 minutes | 2–4 hours | Varies |
| Sludge Characteristics | Thick (3–5% solids) | Dilute (0.5–2% solids) | N/A (solid retention) |
| Chemicals Required | Coagulants, flocculants | None | Often none, but pretreatment may require |
| Energy Demand | Moderate (pumps, compressors) | Низкий | High (especially for membranes) |
| Capital & Operating Costs | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Load/Flow Sensitivity | Низкий | Высокий | Середина |
Why DAF Is Superior for Plastic Recycling Wastewater
1. Removes Light, Suspended Contaminants Effectively
DAF is ideal for removing microplastics, label fibers, and oils—contaminants that float or remain suspended due to their low specific gravity. Sedimentation fails in such cases, and filtration alone often fouls quickly if not preceded by a proper primary treatment.
2. High Efficiency in a Smaller Footprint
DAF requires significantly less space than sedimentation tanks due to shorter retention times and higher surface loading rates. This is a major advantage for industrial facilities with limited real estate or retrofit constraints.
3. Produces Thicker, More Manageable Sludge
DAF yields a more concentrated sludge (3–5% solids), reducing the volume to be dewatered and disposed. In contrast, sedimentation generates dilute sludge, increasing downstream handling costs.
4. Operational Stability and Flexibility
DAF systems are less affected by fluctuations in flow or contaminant concentration. They offer fast startup, rapid response to load changes, and consistent effluent quality—ideal for recycling plants with batch-based or variable operations.
When Sedimentation or Filtration May Be Preferable
While DAF offers numerous advantages, alternative technologies may still be appropriate in certain scenarios:
- Седиментация is suitable when dealing with simple, heavy particulate loads (e.g., grit, sand) and where space is abundant.
- Фильтрация, especially membrane technologies (e.g., UF, RO), is essential for achieving advanced water reuse or discharge standards—but typically functions best as a polishing step after DAF, not as primary treatment for high-solid effluents.
Process Illustration: DAF in Action
- Коагуляция/Флокуляция – Chemicals are added to promote particle agglomeration.
- Насыщенность воздуха – Recycled clean water is pressurized and infused with air.
- Bubble Release – Air-saturated water is released into the DAF tank, forming microbubbles.
- Flotation – Bubbles attach to particles, lifting them to the surface.
- Skimming – A mechanical skimmer removes the floating sludge.
- Clean Water Discharge – Clarified water exits from the bottom for reuse or discharge.
(Consider adding a diagram here for visual explanation.)
Conclusion: A Smart Investment for Sustainable Water Management
For industries like plastic recycling that generate wastewater with low-density, hard-to-settle contaminants, Флотация растворенным воздухом (DAF) is clearly the superior choice. It delivers:
- Higher efficiency in removing oils, greases, microplastics
- Smaller system footprint
- Lower sludge management costs
- Better adaptability to fluctuating loads
Compared to sedimentation and filtration, DAF offers a unique combination of performance, flexibility, and long-term value. When combined with downstream filtration, it forms the backbone of an efficient, modern water treatment system.
📌 Interested in how a DAF system can fit your plant’s specific requirements?
Learn more or request a consultation:
👉 Efficient DAF Water Treatment for Plastic Recycling – Rumtoo