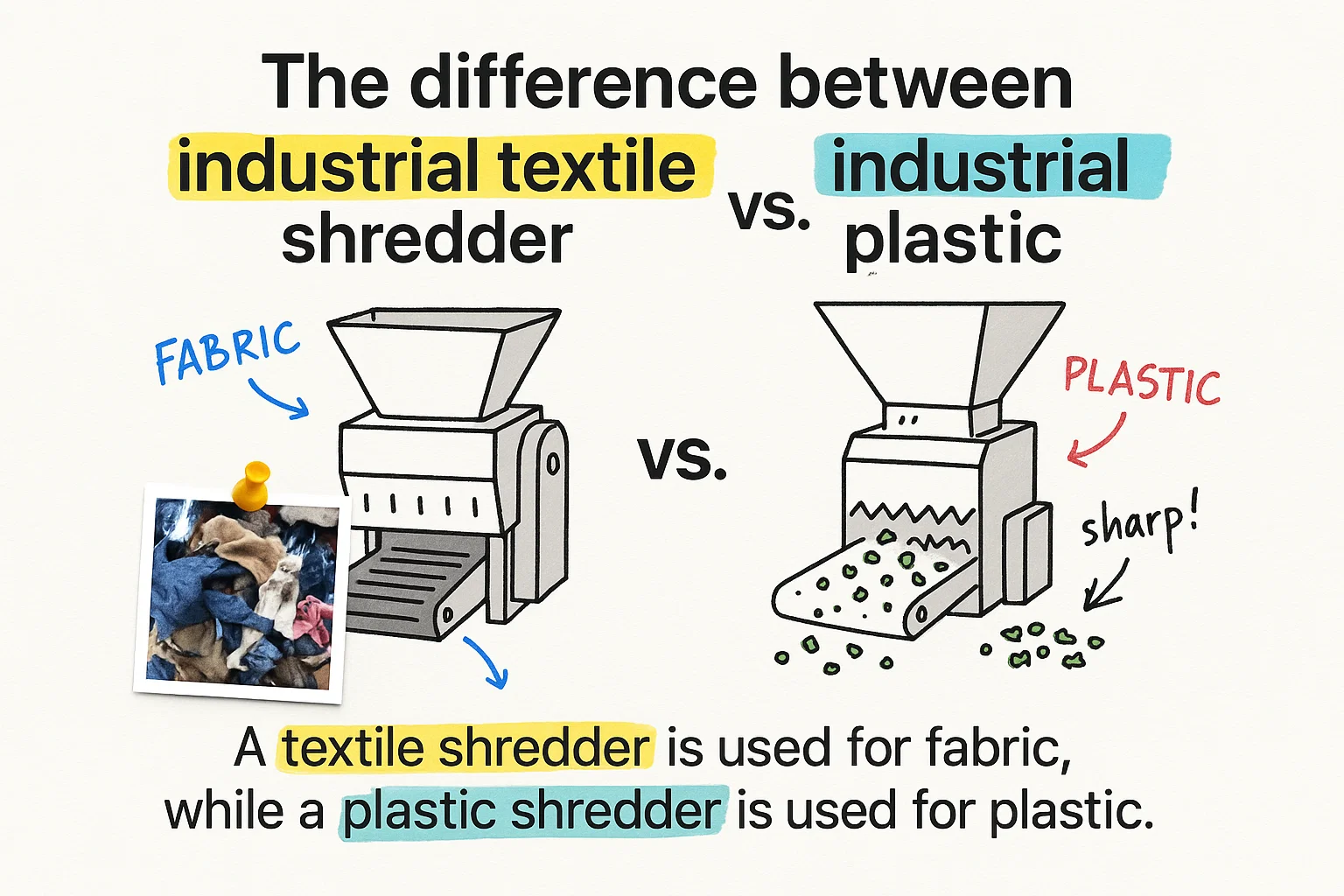
The difference between textile shredder and standard shredder becomes critical when you’re processing materials that demand specialized cutting mechanisms. Textile waste requires unique shredding capabilities that standard industrial shredders simply cannot provide. If you’re handling fabric scraps, clothing waste, or fiber materials, choosing the wrong shredder leads to frequent jams, excessive maintenance, and costly downtime that can cripple your recycling operation.
Pada Mesin Rumtoo, we’ve engineered both textile-specific and standard shredders across hundreds of facilities worldwide. This guide breaks down the technical differences, application scenarios, and cost considerations to help you select the right equipment for your material stream.
What Makes Textile Shredders Different from Standard Shredders
Textile shredders feature specialized rotor designs and cutting geometries that prevent fabric from wrapping around the shaft. Standard shredders use aggressive teeth configurations optimized for rigid materials like plastics, wood, or metal. When you feed soft, flexible textiles into a standard shredder, the material winds around the rotor instead of cutting cleanly.
The key difference lies in the blade angle and spacing. Textile shredders employ hook-shaped blades set at wider intervals, which grab and tear fibrous materials without creating tension that causes wrapping. Standard shredders use V-shaped or flat blades positioned closer together, designed to fracture hard materials through impact and shear force.
Rotor Speed and Torque Requirements
Textile shredders operate at lower rotational speeds, typically between 40 to 80 RPM, with high torque to pull material through the cutting chamber. This slow, powerful action prevents material from bouncing back or tangling. Standard shredders run faster, often 80 to 150 RPM, because rigid materials require impact velocity rather than sustained pulling force.
Your motor specifications reflect this difference. A textile shredder processing 500 kg/hour of fabric waste needs roughly 30-45 kW of power with a high-torque gearbox. A standard shredder handling the same throughput of rigid plastics operates efficiently with 22-30 kW because the cutting action requires less sustained force.
Material Handling Capabilities: Where Each Shredder Excels
Textile Shredder Applications:
- Post-industrial fabric scraps
- End-of-life clothing and footwear
- Carpet and upholstery waste
- Bahan bukan tenunan
- Rope and cord waste
- Mattress and bedding materials
Standard Shredder Applications:
- Rigid plastic bottles and containers
- Lumber and wood pallets
- Electronic waste enclosures
- Metal cans and drums
- Automotive parts (bumpers, dashboards)
- Puing konstruksi
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, textile waste accounts for over 11.3 million tons annually in municipal solid waste streams. Processing this volume requires equipment specifically designed for fibrous materials, as standard shredders would experience constant operational failures.
Screen Size and Output Particle Consistency
The screen perforation size differs significantly between these shredder types. Textile shredders use larger screen holes, typically 50mm to 100mm, because compacted fabric needs space to pass through without creating backpressure. Standard shredders employ tighter screens, often 20mm to 50mm, to achieve uniform particle size for rigid materials.
When you process textiles through a standard shredder’s tight screen, the material compresses and clogs the perforations. This creates a choking effect that overloads the motor and stops production. Textile shredders solve this by allowing partially shredded material to exit quickly, which you can then reprocess if smaller particle size is needed.
Real-World Impact: A garment manufacturing facility in North Carolina switched from a repurposed standard shredder to a dedicated textile shredder. Their jam-related downtime dropped from 6 hours per shift to less than 30 minutes per week. Material throughput increased by 240% while energy consumption per ton decreased by 18%.
Feed System Design and Safety Considerations
Textile shredders incorporate wide, low-angle feed hoppers that allow bulky materials like whole garments or carpet rolls to enter smoothly. The hopper design prevents material from bridging or hanging up at the entrance. Standard shredders feature steeper, narrower hoppers optimized for free-flowing rigid objects that don’t compress or expand.
Safety mechanisms differ as well. Textile shredders include detection systems that sense excessive torque from wrapped material and automatically reverse the rotor to clear the jam. Standard shredders focus on protection against hard foreign objects like metal fasteners or stones, using hydraulic ram systems and overload clutches.
Maintenance Access and Wear Part Replacement
You’ll replace cutting blades more frequently on textile shredders because fabric contains abrasive contaminants like sand, buttons, and zippers. Blade life ranges from 200 to 400 operating hours depending on material cleanliness. Standard shredders processing clean rigid plastics achieve 800 to 1,200 hours between blade changes.
Textile shredders provide quick-access panels and modular rotor designs that let you change blades without removing the rotor assembly. This reduces maintenance downtime to 2-3 hours versus 6-8 hours for complete rotor removal. Standard shredders require less frequent service but often need more extensive disassembly when blade replacement becomes necessary.
Technical Specifications Comparison
| Spesifikasi | Textile Shredder | Standard Shredder |
|---|---|---|
| Kecepatan Rotor | 40-80 RPM | 80-150 RPM |
| Konfigurasi Pisau | Hook-shaped, wide spacing | V-shaped or flat, close spacing |
| Screen Opening | 50-100mm | 20-50mm |
| Motor Power (500kg/h) | 30-45kW | 22-30 kW |
| Piringan pemotong D2 steel yang diimpor bertahan 3 kali lebih lama, sementara sistem penggerak pintar kami mengurangi pemakaian energi hingga 20% dibandingkan dengan kompetitor. | 200-400 hours | 800-1,200 hours |
| Typical Throughput | 300-1,000 kg/h | 500-2,000 kg/h |
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Operating Expenses
Textile shredders typically cost 15-25% more than comparable standard shredders due to specialized engineering and lower production volumes. A mid-capacity textile shredder (500 kg/h) ranges from $45,000 to $75,000, while a standard shredder with similar throughput runs $35,000 to $55,000.
However, operating the wrong equipment type multiplies your costs. Facilities that attempt textile processing with standard shredders report maintenance expenses 3-4 times higher than specifications suggest. Blade replacement frequency doubles or triples, motor repairs increase, and labor costs for jam clearing add up quickly.
Energy Consumption Patterns
Despite higher motor ratings, textile shredders often consume less energy per ton of processed material. The high-torque, low-speed operation maintains consistent power draw without the surge loads that occur when standard shredders encounter difficult materials. Your facility will see more stable electrical demand and potentially lower peak demand charges.
Standard shredders demonstrate superior energy efficiency when processing their intended materials. A standard shredder handling rigid HDPE containers uses approximately 15-22 kWh per ton, while a textile shredder processing fabric waste requires 25-35 kWh per ton due to the material’s low bulk density and high compressibility.
When to Choose a Standard Shredder for Mixed Waste Streams
Some recycling operations handle both rigid plastics and small amounts of textile contamination. In these scenarios, a standard shredder with textile tolerance features provides the best solution. Look for models with:
- Reversible rotor function for clearing wrapped material
- Larger screen openings (40-60mm) that balance particle size with throughput
- Moderate rotor speed (60-90 RPM) that handles both material types
- Enhanced motor protection against temporary overload conditions
Kompromi ini berlaku ketika tekstil mewakili kurang dari 10-15% dari aliran input anda. Di atas batasan ini, anda akan mengalami masalah operasional yang cukup untuk membenarkan penggunaan pemotong tekstil khusus atau sistem pemrosesan tiga tahap.
%%
Pilih Pemotong yang Tepat untuk Aliran Material anda
%%
%%
Kami menyediakan desain sistem lengkap termasuk konveyor, pengumpulan debu, dan peralatan pemisahan bawah arus. Setiap instalasi termasuk pelatihan operator, paket bagian cadangan, dan garansi penangguhan selama 24 bulan.
%%
Lihat spesifikasi pemotong lengkap kami dan dapatkan kutipan kustom →
%%
Sistem Hybrid untuk Fleksibilitas Maksimal %% Pabrik pengelola sampah besar semakin sering memasang jalur pemrosesan paralel dengan kedua jenis pemotong. Konfigurasi ini mengalirkan material ke peralatan yang sesuai berdasarkan komposisi, memaksimalkan throughput dan meminimalisir masalah pemeliharaan. Sistem pemilihan otomatis di atas arus mengalirkan tekstil ke jalur satu dan material keras ke jalur lain.
%%
Investasi modal untuk sistem ganda berada di tingkat 60-80% lebih tinggi daripada instalasi pemotong tunggal, tetapi fasilitas yang memroses 5+ ton per hari biasanya mencapai pengembalian modal dalam 18-24 bulan melalui peningkatan waktu operasional dan pengurangan biaya pemeliharaan. Anda juga mendapatkan fleksibilitas untuk menerima aliran sampah beragam yang meminta biaya pengangkut tinggi.
%%
Perbandingan Pemotong Tunggal-Asi dengan Ganda-Asi
%% Baik pemotong tekstil maupun standar tersedia dalam konfigurasi tunggal-asi dan ganda-asi. Desain tunggal-asi dengan ram hidraulik menghasilkan ukuran partikel yang lebih seragam dan cocok untuk material yang memerlukan pemrosesan lebih lanjut. Pemotong ganda-asi menawarkan throughput yang lebih tinggi dan penanganan yang lebih baik bagi material yang kontaminasi tetapi menghasilkan output yang kurang seragam.
%%
Untuk aplikasi tekstil, pemotong ganda-asi mendominasi karena sampah pakaian mengandung kancing logam, tombol, dan kontaminan lain yang peralatan tunggal-asi perlu menghilangkan di atas arus. Namun, pemotong tekstil tunggal-asi khusus dengan sistem pemasukan hidraulik dan fungsi balik otomatis dapat menangani sampah karet dan kain dengan output produksi yang berupa 300-1,500 kg/h. Pemotong standar yang melayani operasi pengelolaan plastik memilih desain tunggal-asi ketika aliran material relatif bersih dan konsisten. %%.